Week 9
- gabriellakaren3
- May 23, 2019
- 2 min read
Class Works
1. Presentation
Dadaism
What is Dadaism?
- Dadaism is an artistic movement in modern art that started around World War I.
- Its purpose was to ridicule the meaninglessness of the modern world.
- Dadaism greatly influenced movements such as surrealism, action painting, pop art, installations, happenings and conceptual art. It favored going against the standards of society.
- The name itself is reflection that the art was designed to seem meaningful when it is in fact a reflection of how overvalued societal norms and expectations had become. The word "Dada" in and of itself has no meaning.
CHARACTERISTICS
- Corrosive, confrontational, provocative
- Uses elements of automatism and chance
- Uses physical elements from the real world, such as newspapers, advertisements, and junk to relate its artworks to reality
- Was more of a protest movement than a style of art
- Highly satirical
- Sought to offend rather than to impress
- Believed that the idea behind the art is more important than the physical results of the artwork itself (led to conceptual art)
- Could be made from anything, no matter how ordinary.
- The Dadist technique of dislocating objects from their normal context and representing them as art - was used widely by later assemblage and Pop-artists.
- Another Dadaist technique was photomontage - used especially by Berlin Dadaists like Raoul Hausmann
- Refining the Cubist idea of collage, Dada artists used these clippings to construct puzzling or strikingly incongruous juxtapositions of images and letters. The ultimate Dada collage artist was Kurt Schwitters in Hanover, whose works were made from urban detritus like litter, bus tickets, sweet wrappings and other scraps.
Other Famous Dadaists:
Jean Arp (1887-1966): Poet and Sculptor
Highly experimental, he explored geometric abstraction as well as Dadaist styles, and later joined the Surrealist movement.
Max Ernst (1891-1976): Painter, Sculptor, Graphic artist, Poet
He became one of the pioneers of both Dada and Surrealism. During his Surrealist phase he was noted for his invention of frottage and decalcomania
Raoul Hausmann (1886-1971): Painter, Photographer
He pioneered the technique of photomontage - the art of affixing and juxtaposing photographs or other "found" illustrative material onto a flat surface
DEFINITION OF PHOTOMONTAGE, FROTTAGE, COLLAGE, GRATTAGE
- Photomontage is the process and the result of making a composite photograph by cutting, gluing, rearranging and overlapping two or more photographs into a new image.

- In frottage, the artist places a piece of paper over an uneven surface then marks the paper with a drawing tool (such as a pastel or pencil): thus creating a rubbing. The drawing can be left as it is or used as the basis for further refinement. This method is developed by Max Ernst.
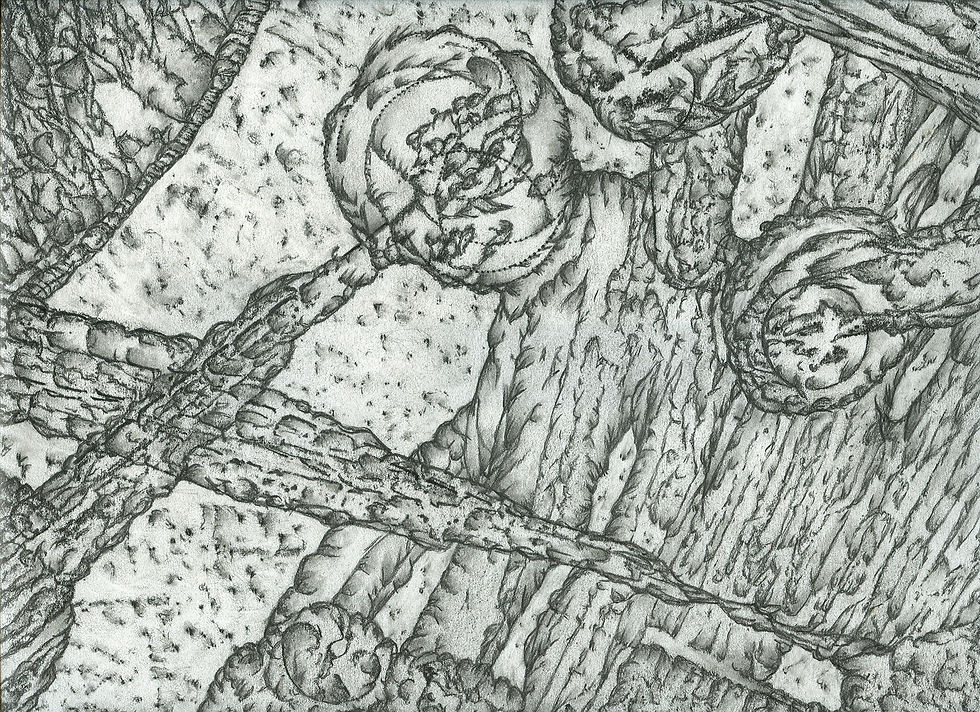
- Collage is a technique of an art production, primarily used in the visual arts, where the artwork is made from an assemblage of different forms, thus creating a new whole. It may sometimes include magazine and newspaper clippings, ribbons, paint, bits of colored or handmade papers, portions of other artwork or texts, photographs and other found objects, glued to a piece of paper or canvas.

- Grattage is a surrealist painting technique that involves laying a canvas prepared with a layer of oil paint over a textured object and then scraping the paint off to create an interesting and unexpected surface

2. Collages
Exercise 1

Exercise 2
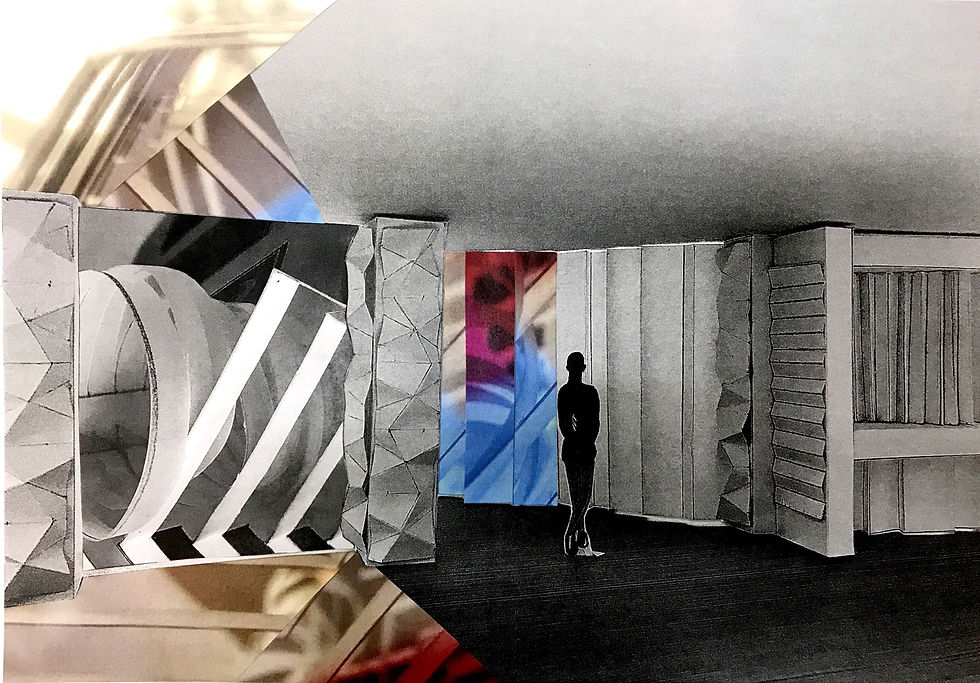
Exercise 3

Exercise 4





























Comments